
Full transparency from Sweden
Mark Sollman, product manager, Mimaki Europe

11th January 2022
Innovation in Textiles
|
Europe
With the all-important COP26 Climate Change Conference having taken centre stage in November, there is no time like the present for the fashion world to rally together in stepping up sustainability efforts and getting carbon emissions under control, says
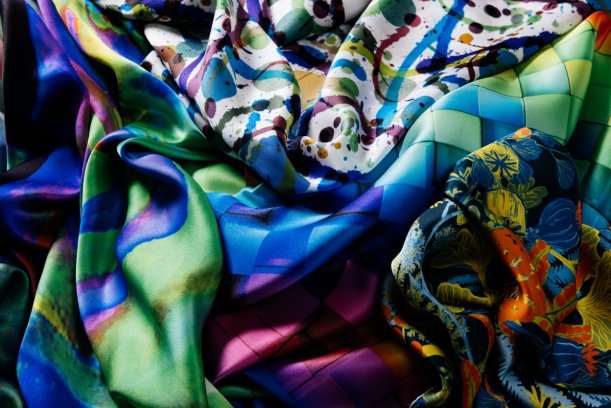
Globally, the fashion industry is now estimated to account for around 10% of greenhouse gas emissions and 20% of wastewater , making the pursuit of greener production methods more pertinent than ever before. Thankfully, we are seeing a new era of production enter the fashion arena, with the increasing emergence of technologically advanced, highly automated microfactories.
Along with reducing unnecessary waste through on-demand production, microfactories have a smaller ecological footprint than traditional garment production and require no water use during the production process, making it not only a faster solution, but a greener one too.
FESPA 2021
Last year’s FESPA saw Mimaki team up with fashion designer Carolina Guzman to bring her designs to life in real time at the show, setting up its own working microfactory live on-site to take her designs from screen to garment within just a day. Guzman’s designs were created using Mimaki’s TS100-1600 sublimation printer, before being transferred to textile, digitally cut and finally pieced together. Devised with a string of ethical and environmental objectives threaded throughout, the microfactory also exclusively utilised eco-friendly Greentex fabric, and any remaining material was donated to Sheltersuit – a wind- and waterproof coat that can be transformed into a sleeping bag, which is provided free of charge to homeless people and refugees.
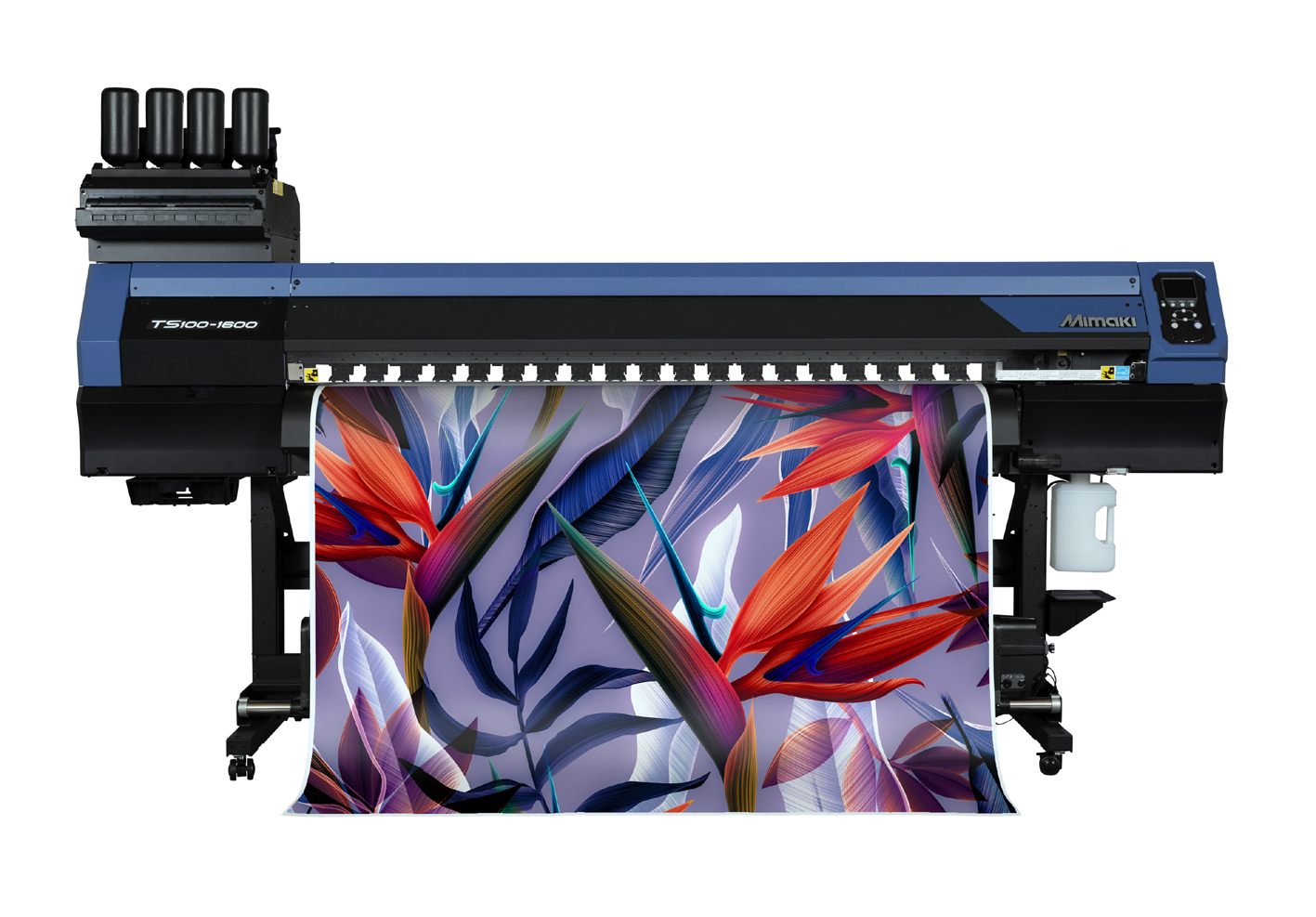

Through working with a number of strategic partners – including transfer printing expert, Klieverik, paper solutions specialist, Neenah Coldenhove and digital cutting equipment provider, Summa – Mimaki was able to produce a collection of unique, high-quality garments live on the stand during the tradeshow, demonstrating to visitors from more than 100 countries some of the key reasons that microfactories seem set to change the future of fashion.
Versatility
Where traditionally, apparel manufacturing has centred on a production chain model of sourcing materials and producing garments in bulk, microfactories are now enabling on-demand, on-location production, making it possible to create everything from unique, one-off pieces and samples right through to entire product runs – all at unprecedented speeds. This means greater flexibility and customisation, enabling designers to modify or update designs and respond to market trends as they occur.
The microfactory setup brings production in-house and on-demand, minimising the cost of not only storing stock, but also of shipping it and responsibly disposing of unsold items. Where recent geopolitical events have highlighted the fragility of global supply chains, microfactories offer a unique independence from these systems, empowering garment manufacturers to future-proof their businesses, become less reliant on external systems and suppliers, and reduce the risk of disruptions.
Boosted bottom line
Facilitating savings in a whole line of resources, from physical storage and production space to time and energy, microfactories ultimately have the potential to significantly increase profitability for garment manufacturers, with the additional benefit of being easily scalable as production increases. Perhaps even more compelling, however, are the environmental considerations. Demonstrated on a small scale through Mimaki’s recent project, the environmental benefits inherent to microfactory production will have an even greater impact as it becomes more prolific and commonplace throughout the fashion world, with the potential to effect meaningful environmental change as adoption increases in the years to come.
Watch this space.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more