
2019 Composites Industry Award winners announced
Defining a future led by high-rate manufacturing, digital coherence and circularity in Paris.

15th January 2026
Innovation in Textiles
|
Paris
JEC World announced the winners of its 2026 Innovation Awards at a special event in Paris on January 12th, recognising collaborative, forward-looking projects that demonstrate the transformative potential of composite materials across global industries.
The winners in the individual categories are as follows:
Aerospace Parts
In France, Daher has reimagined the traditional metallic aircraft wing rib, working closely with the Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology, Victrex in the UK, Cetim in France and AniForm Engineering in the Netherlands to create a highly loaded thermoplastic rib formed from carbon fibre reinforced LMPAEK.
LMPAEK (low-melt polyaryletherketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer engineered to melt at a lower temperature than standard PEEK (polyetheretherketone) or PAEK (polyaryletherketone) grades. This lower melting point gives manufacturers a wider and more stable processing window, which is particularly valuable in the automated fibre placement (AFP), press forming, stamp forming and welding of carbon-fibre laminates.
LMPAEK maintains the hallmark properties of the PAEK family – toughness, chemical resistance, fatigue resistance and high temperature capability – but offers greater processing efficiency, lower energy demands and improved weldability.
The result, shaped through advanced AFP and infrared welding, achieves the dual objectives of weight reduction and high-rate processing.
Aerospace Process
Sauber 4.0 represents a fully networked manufacturing approach for large and complex aerospace components, combining resin transfer moulding with digitisation and advanced tooling and preforming technologies. Germany’s CTC, an Airbus company, has brought together an extensive German consortium that includes research institutes, technology providers and energy-modelling specialists to achieve this. The programme brings together inductively heated tooling, advanced preforming and a digitalised RTM process designed to support both ecological and economic targets in next-generation wing production.
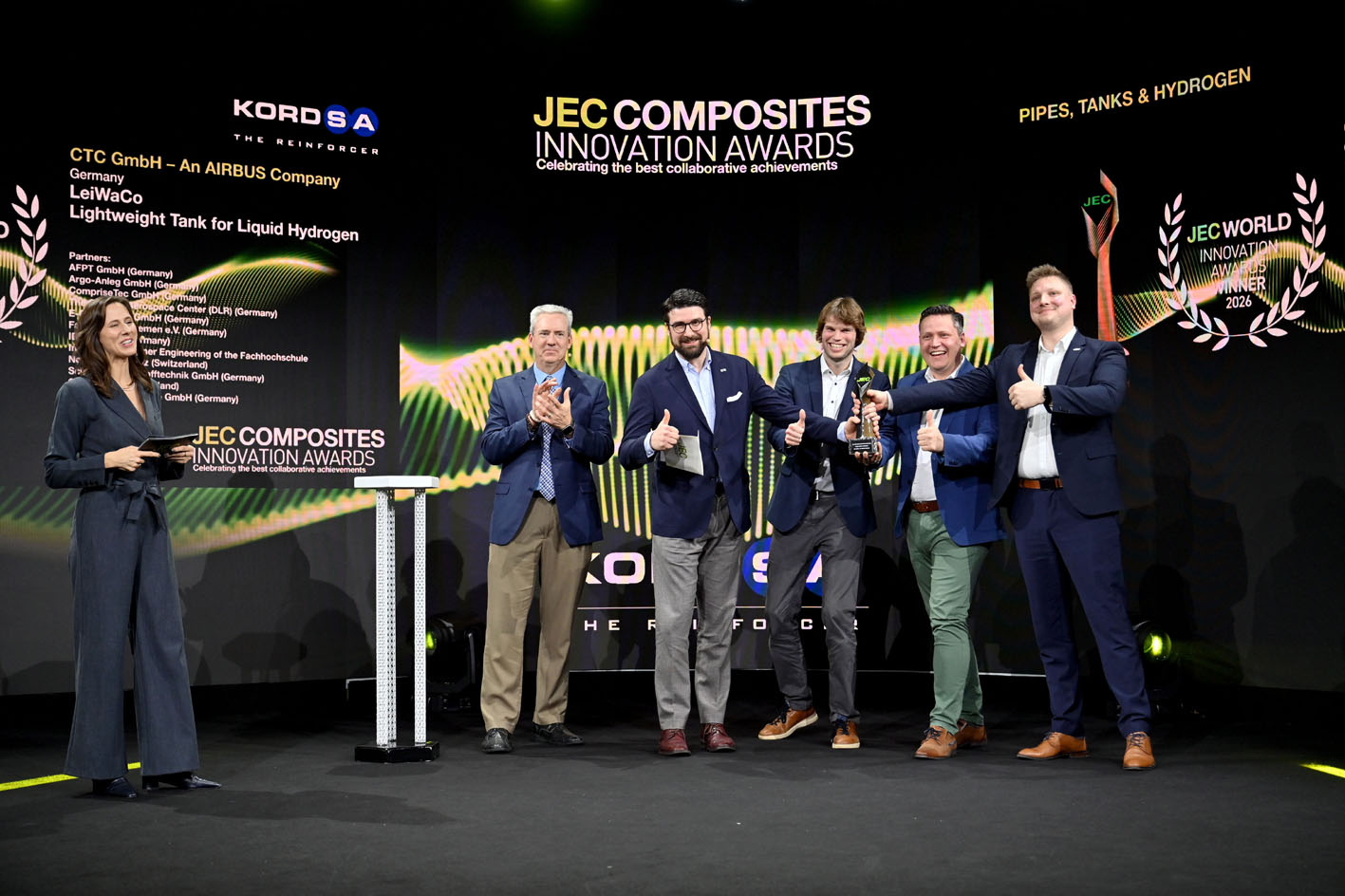

The project enables the transition from small CFRP parts to large, integral wing structures suitable for next-generation single-aisle aircraft.
Automotive and Road Transportation Parts
BMW M has partnered with Bcomp in Switzerland, SGL Technologies and PPG Wörwag in Germany and Cobra in Thailand to advance flax-based natural fibre composites for both interior and exterior applications.
Proven under motorsport conditions and supported by improved resin systems and coatings, the materials offer a substantial reduction in production emissions while aligning with BMW’s wider sustainability strategy.
Automotive and Road Transportation Process
A lightweight, load-bearing battery housing made from glass fibre reinforced thermoplastics has been developed by Chemnitz University of Technology and partners for large-scale electric vehicle production. By combining commercially available long and continuous-fibre semi-finished products and processing them through high-speed compression moulding, the project achieves cycle times of under two minutes. The resulting component delivers a 15% weight reduction and approximately 25% lower lifecycle emissions compared with an aluminium die-cast reference, while enabling waste-free production and high structural performance suitable for mass manufacture.
Circularity and Recycling
A collaborative project between Airbus, Daher, Toray and Tarmac Aerosave demonstrates a practical circular reuse strategy for aerospace thermoplastic composites. End-of-life A380 pylon covers made from carbon fibre reinforced PPS are repurposed into new structural components for the A320neo, extending material life and avoiding landfilling of high-performance composites. The initiative proves the industrial feasibility of thermoplastic recycling and establishes a scalable model for circularity across future aircraft programmes.
Digital, AI and Data
In Australia, the University of Southern Queensland, working with MEMKO, Dassault Systèmes and Boeing Australia, has created a continuous digital thread for the repair and manufacture of composite aerospace structures. The system integrates inspection, automated patch definition, scarfing strategies, manufacturing data and return-to-service validation.
Maritime Transportation and Shipbuilding
Loiretech Ingénierie in France, working with partners across Greece, Cyprus, France, Bulgaria and the UK, has developed CoPropel, a composite propeller designed to adapt its pitch under load through tailored fibre orientation. Embedded optical fibres and strain gauges provide continuous structural-health monitoring, while an RTM manufacturing route ensures robust edge protection.
Pipes, Tanks and Hydrogen
Germany’s CTC, collaborating with AFPT, Argo-Anleg, CompriseTec, DLR, E-Cap Marine, Faserinstitut Bremen, IDVA, the Swiss FHNW, Schunk, Suprem and Teijin Carbon Europe, has addressed the challenge of cryogenic microcracking in liquid hydrogen tanks. Through a considered combination of thermoplastic matrices, optimised lay-ups and manufacturing developments, the LeiWaCo project delivers a demonstrator that could underpin future hydrogen mobility.
Railway Vehicles and Infrastructure
UK company Composite Braiding has collaborated with Amey, Connected Places Catapult and BCIMO to produce a composite twin-track cantilever for railway electrification infrastructure.
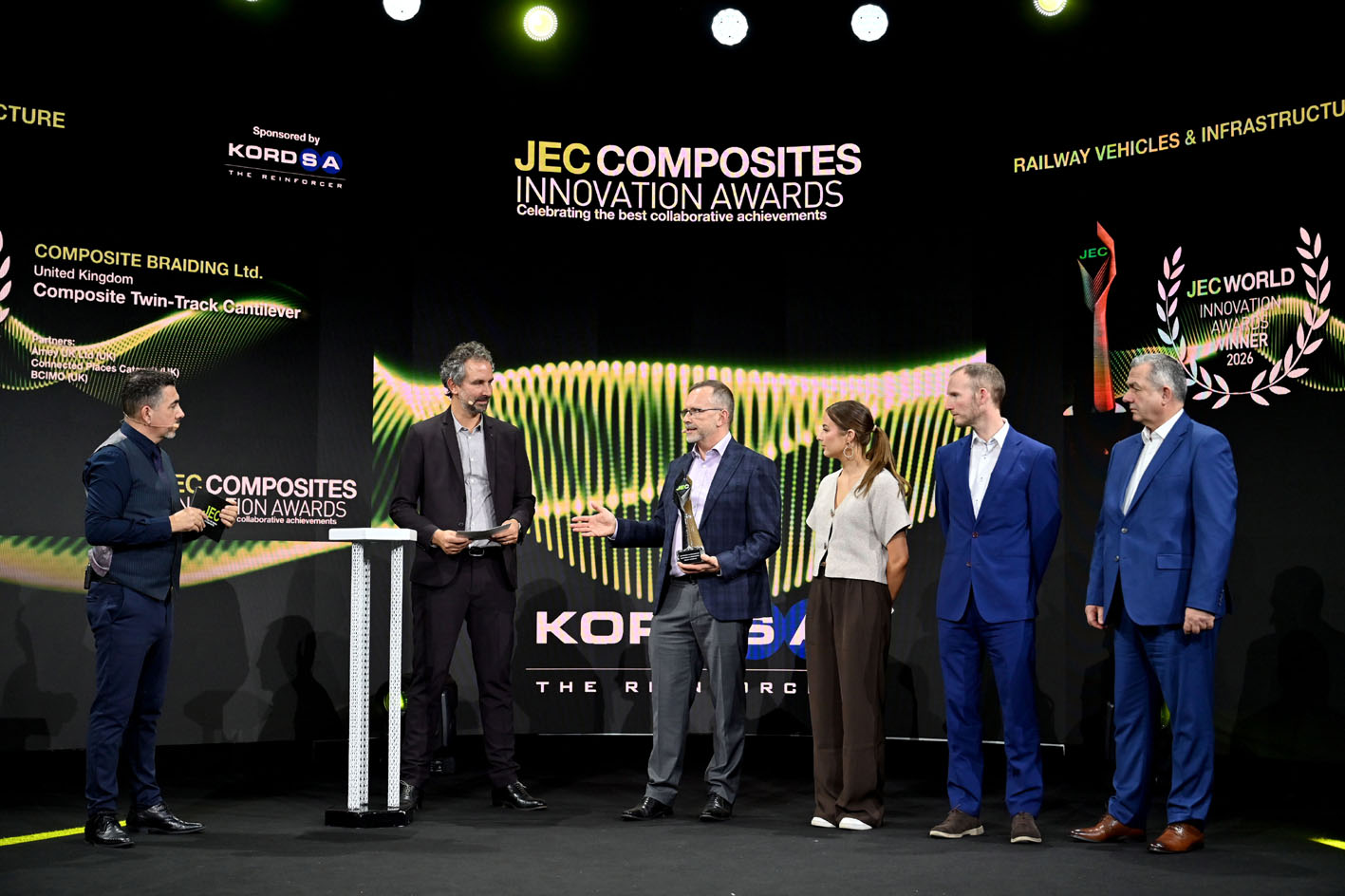

Using braided thermoplastic composites consolidated at high speed, the partners have demonstrated an 80% mass reduction and a step-change in installation efficiency.
Renewable Energies
Turkey’s Metyx, working with Itech Solar and the Middle East Technical University’s Centre for Solar Energy Research, has introduced a composite photovoltaic module for vehicles that replaces glass with a transparent glass fibre composite front sheet and a carbon fibre sandwich back. Lightweight, impact resistant and suitable for curved surfaces, the design broadens the horizon for vehicle-integrated solar power.
Sports, Leisure and Recreation
Germany’s Fenix Composites, collaborating with Alformet, Herone and HyJOIN, has introduced a repairable, recyclable road-bike frame made from thermoplastic carbon composite tubes joined to titanium lugs by reversible induction welding. The design allows damaged components to be replaced without discarding the entire frame, demonstrating how performance cycling can embrace longevity.
A new industrial landscape
The 2026 winners represent a composites sector moving confidently towards a future defined by high-rate manufacturing, digital coherence and circularity. Materials are becoming lighter, tougher and more sustainable, manufacturing is becoming leaner, smarter and more automated and collaboration remains the catalyst that moves innovations from laboratory experiments to industrially viable solutions.
In the last 28 years, the JEC Composites Innovation Awards have attracted more than 2,200 participating companies from around the world.
JEC World 2026 will take place from 10 to 12 March 2026 at Paris-Nord Villepinte, bringing together the major players across the entire composites value chain and showcasing the innovations shaping the future of the industry.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more