
Design freedom with FiberAcoustic 450
Hohenstein scientists led by Dr. Jan Beringer, in conjunction with Hochschule Reutlingen and Rökona Textilwerk GmbH in Tübingen, have developed innovative test methods to investigate the acoustic and aeroacoustic properties of textile materials.
21st May 2012
Innovation in Textiles
|
Boennigheim
Hohenstein scientists led by Dr. Jan Beringer, in conjunction with Hochschule Reutlingen and Rökona Textilwerk GmbH in Tübingen, have developed innovative test methods to investigate the acoustic and aeroacoustic properties of textile materials.
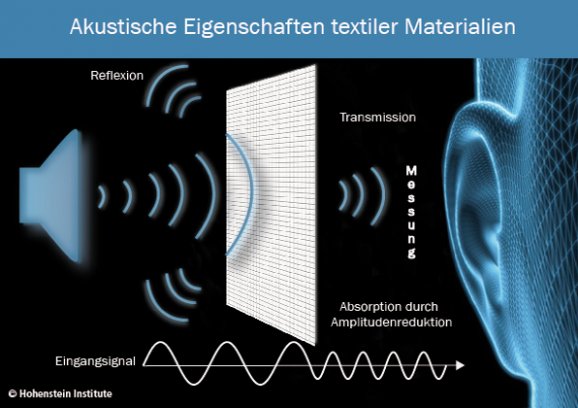
The extent to which a textile material has a sound-absorbing effect and which are the noises that cause wind flow, can now be investigated using acoustic test apparatus at the Hohenstein Institute in Bönnigheim.

“Noise now pervades all parts of our everyday lives and is becoming an increasing source of stress. In addition to the negative effects on the nervous system, studies have shown that it diminishes concentration ability by about 20-30%, reduces work performance, increases accident risks and above all decreases feelings of comfort. Even sounds above 40 decibels corresponding approximately to soft radio music can produce these negative effects,” the researchers explain.
Sound-absorbing textile materials therefore are gaining popularity in the many sectors where sounds are perceived as unpleasant and disruptive. According to Dr Beringer’s team, it is primarily in the interior design and automotive sectors where specifically adapted materials are used to minimise and optimise noises leading to a rise in acoustic comfort.
Sound-absorbing ceilings, partitions, floors and furniture surfaces in public facilities, open-plan offices and exhibition halls as well as technical textiles in vehicle interior linings are all effective measures to counter acoustic disturbances.
During the testing process at the Hohenstein Institute different textile materials are investigated with the acoustic measuring device. The fabric to be tested is clamped in a sample holder between a loud speaker and a measuring microphone. One great benefit here, the researchers say, is the small sample size - fabric samples measuring only 10 x 10 cm are large enough. Measurements are taken within a frequency spectrum of 200 – 20,000 Hz to ascertain the extent (decibels) to which the fabric attenuates/dampens the signal sent by the loudspeaker.
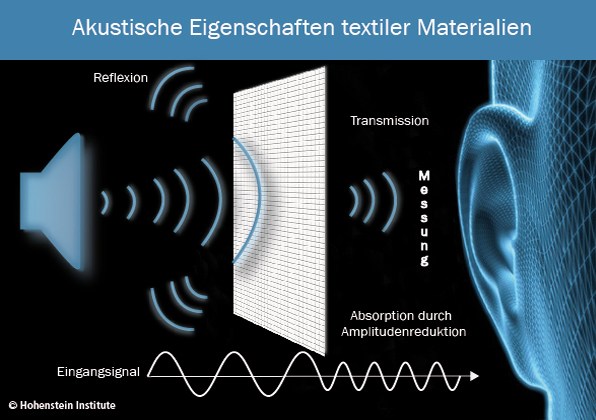
The aeroacoustic test determines the frequency spectra of the often disturbing background noise of textile air flow. The Hohenstein Institute test apparatus is said to be able to investigate virtually all samples ranging from small laboratory samples up to complete components and can simulate wind speeds of up to 140 km/h.
The textile or component is exposed to air flow and a special measurement microphone is then used to record the noise caused by the air flow. This noise is then subject to computer analysis and the corresponding frequencies of the noise are determined. These resulting comparative figures then enable materials to be optimised for the most diverse of uses.
As well as capturing the aeroacoustic properties of textile fabrics, locally-triggered causes of air flow noises can also be determined.
The Hohenstein Institute says this knowledge can then be used to optimise textiles and components even more.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more