
Heathcoat’s ripstop to the Red Planet’s surface
Yesterday marked another achievement in the story of Heathcoat Fabrics’ journey into space, when the Perseverance Rover landed on the red planet.

19th February 2021
Innovation in Textiles
|
Tiverton, Devon, UK
Engineers at Heathcoat Fabrics in the UK’s picturesque county of Devon, recently faced a huge task, creating a parachute material that could withstand extremes of temperature and be strong enough to withstand the force of a supersonic deployment at Mars. Nevertheless, NASA’s Perseverance Rover launched on schedule, on 30 July 2020 from Cape Canaveral Space force Station in Florida, propelled on the start of its seven-month, 480-million-kilometre journey, by an Atlas V rocket.
The talented team at Heathcoat Fabrics tells the full story.
Because of the distance between Earth and Mars, there is an 11-minute delay in any communications, Heathcoat explains. As a result, Perseverance hit the planet's atmosphere without any outside guidance, relying only on autonomous systems. Because the planet's atmosphere is incredibly thin, it does not offer much resistance, barely slowing down the rover travelling within its protective shell.
Mars 2020 is carrying the heaviest payload yet to the surface of Mars, and like all our prior Mars missions, we only have one parachute, and it has to work
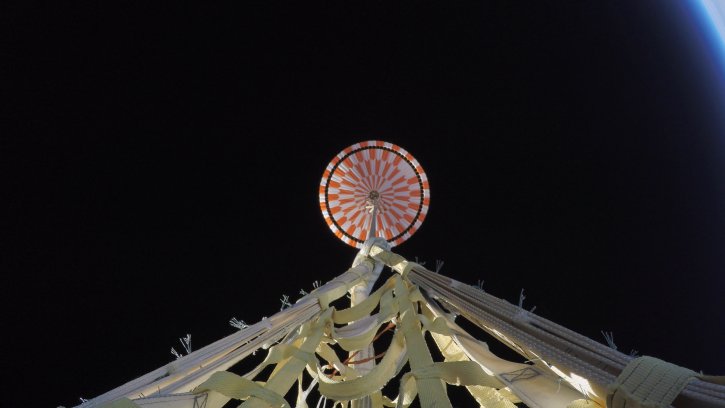
Just four minutes after entering the Martian atmosphere, and still travelling at 20,000km/h per hour (that’s 16x the speed of sound), the rover deployed a world-record breaking parachute to slow it down. "In the thin Martian atmosphere, the parachute is only able to slow the vehicle to about 320km/h,” NASA said at the time.
The impact shock of ‘slamming on the brakes’ at hypersonic speeds is incredible, Heathcoat enlightens, with the single parachute achieving a 98.4% reduction in speed. This is the moment that not only NASA control were holding their breath, but also the team of fabric engineers and production staff at Heathcoat’s manufacturing site in Tiverton, who were responsible for developing and producing the fabric for the parachute used for the Mars 2020 mission.
How did a Devon-based textile manufacturer become an important supplier to the world’s biggest space agency? Peter Hill, Director of the woven fabrics business at Heathcoat, explains: “It began with us showing our capabilities at a Parachute Industries Symposium in the US, around 15 years ago. Heathcoat Fabrics make the lightest, strongest and most resilient parachute fabrics, and we were keen to prove it.”
The commitment to making new concept fabrics and presenting them to an industry audience led to more and more people finding out about our capabilities, and a request came in for something bespoke.

The Heathcoat Fabrics engineers faced quite a task, having to create a material that can withstand huge extremes of temperature and still be strong enough to withstand the force of a supersonic deployment at Mars.
"Mars 2020 is carrying the heaviest payload yet to the surface of Mars, and like all our prior Mars missions, we only have one parachute, and it has to work," observed John McNamee, Mars 2020 project manager.
A key to Heathcoat’s incredibly strong and ultra-lightweight parachute fabrics are its unique Heathcoat Advanced Yarns, customised weaving and specialised fabric finishing processes.

One of Heathcoat’s graduate development engineers explains the hidden strengths built into its DecelAir fabrics and some of the challenges the development team faced: “Our latest parachute fabrics are the strongest, lightest and most heat resistant parachute fabrics ever produced. Heat resistance is vital for parachutes destined for space as they need to be baked at high temperature to ensure that microorganisms from Earth do not contaminate other planets.”
“For the Mars2020 mission JPL-NASA had very specific requirements so that the parachute would survive deployment at supersonic speeds, which we achieved through processing on a dedicated range of equipment.”
After high-speed weaving, washing and colouration the fabric is processed with a special finish to aid rapid deployment followed by meticulous visual inspection of every centimetre of the fabric. The fabric is then tested to ensure that it meets all of NASA’s exacting requirements before being packed into specially manufactured protective transport crates.

“It is an incredibly emotional moment, when you know that millions of people around the world are holding their breath, waiting for news of a successful touchdown, and that part of that success is down to the efforts of our fantastic team here in Tiverton,” said Richard Crane, Heathcoat’s Technical Director.
In addition to exploratory space uses, DecelAir Superlight, Heathcoat’s commercial parachute fabric brand, is also successfully being used for drone-recovery parachutes, paraglider and skydiver reserve parachutes.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more