
$125k to grow Rhode Island composites industry
New nanofibre improves the durability of automotive tyres, hoses and belts.

13th April 2022
Innovation in Textiles
|
Japan
Teijin Frontier is introducing a new staple polyester nanofibre for the reinforcement of rubber used in products including automotive tyres, hoses and belts,
The company has also just developed a proprietary system for calculating CO2 emissions generated by its polyester fibre production processes.
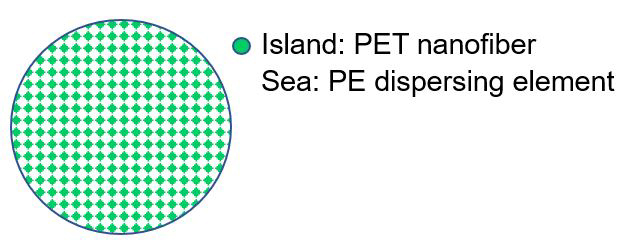
The new nanofibre incorporates both polyester and polyethylene polymers which are combined in a proprietary sea-island composite cross section. Different polymers are used for the “sea” and “island” parts to improve rubber reinforcement. A polyester nanofibre with a diameter of either 400nm or 700nm is used as the island as reinforcing material and the surrounding sea part is made with polyethylene, which mixes easily with rubber. Mixing takes place at the molecular level, which enables thousands more nanofibres to be evenly dispersed for better reinforcing with a relatively small amount of material.
The length of the new staple nanofibre is just 1mm or less, but the aspect (length-to-diameter) ratio is high thanks to the small diameter, which contributes to the reinforcing. In addition, the fibre’s short length prevents entanglement and twisting, and additionally helps to disperse the fibres and rubber evenly. The fibere forms continuous lines or surfaces, rather than dispersed clumps. In actual use, the fibres rather than the rubber absorb deformation stress, resulting in more durable rubber products.
Since the new staple nanofibre exhibits higher reinforcing performance compared to conventional products, it can reduce the polymerization process. The shorter fibre eliminates the need for surface treatment, which prevents it from intertwisting like cotton. Both attributes help to reduce environmental load, including less greenhouse gas emissions.
Elasticity
When used in automotive tyres, it increases elasticity and reduces resistance, so it should help to improve fuel efficiency and reduce noise. It is also expected to improve the elastic modulus and durability of automotive hoses and belts, which has been difficult to achieve until now.
Staple fibres are used to strengthen rubber in products required to withstand repeated deformation and abrasion. Conventionally, this has been achieved by adjusting fibre strength and length – the latter generally to between several millimetres and several tens of millimetres. Increased length, however, leads to entanglement and twisting when the fibre is kneaded into the rubber, which reduces strength due to less efficient fibre dispersal. Meanwhile, growing environmental concerns are raising demands for reduced molecular weights and surface treatments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Teijin Frontier will start production in 2023 and expects sales to reach nearly $8.2 million by its fiscal year ending in March 2028.
Emissions calculator
Teijin proprietary system for calculating CO2 emissions generated by the company’s polyester fibre production processes is meanwhile expected to be used for full lifecycle assessments foing forward.
It calculates CO2 emissions based on data from the company’s manufacturing bases and also compares differences in emissions between petroleum-derived fibres and recycled fibres to quantitatively evaluate the effect. The system additionally helps to clarify which processes need to be improved to further reduce environmental loads and better measures for reducing CO2 emissions can be considered.
Teijin Frontier has already begun using the system to evaluate emissions from polyester filaments and staple fibres production, and will gradually expand the scope to include weaved and dyed textiles products. The company also plans to encourage partners to adopt the system.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more