
Responding to demand for Naia
New study shows CDA-based materials disintegrate and biodegrade in the ocean in just months.
8th February 2022
Innovation in Textiles
|
Paris
At his week’s Première Vision (PV) currently taking place in Paris, as well as online (February 8-10), Eastman is showcasing new fabrics based on its sustainably-sourced Naia cellulosic fibre.
Having debuted at this event only three years ago, the versatile Naia offerings have been expanded as the company has collaborated with dozens of brands and numerous value-chain partners worldwide.
Naia is produced from 60% sustainably sourced wood pulp and 40% hard-to-recycle waste material diverted from landfills or incinerators, with a low carbon footprint in a closed-loop process where solvents are safely recycled back into the system for reuse.
It can be produced at scale and with full traceability from tree to fibre and is available in filament yarn form, featuring a silky hand, rich lustre and fluid drape that can be used to create fashionable womenswear garments, or as a staple fibre, which is inherently soft and quick drying. Its reduced pilling properties make it ideal for loungewear. It blends well with other eco-friendly materials such as lyocell, modal and recycled polyester.
“We have experienced strong growth due in large part to the quality of our offerings, the inherent sustainability of Naia and a strong network of global partners,” said Eastman marketing director Ruth Farrell. “Collaboration is key to creating measurable impacts in sustainable fashion. Numerous brands are working with us to meet their sustainability goals, and we’re helping our mill partners get their products to market.”
Ocean disintegration
Eastman has also recently received further scientific evidence that cellulose diacetate (CDA)-based Naia disintegrates and biodegrades in the ocean within months.
Researchers from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), a leading, independent non-profit organisation dedicated to ocean research led the study, which was published in December and demonstrated that CDA-based materials disintegrate and biodegrade in the ocean orders of magnitude faster (months) than previously reported (decades).”
CDA is largely derived from wood pulp, making it biobased. Naia cellulosic fibre is responsibly sourced from sustainably managed pine and eucalyptus forests, and it is produced in a safe, closed-loop process where solvents are recycled back into the system for reuse.
“These materials are breaking down on timescales of months,” said co-author Collin Ward, assistant scientist in the Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Department at WHOI. “This challenges the perception that they persist for decades.”
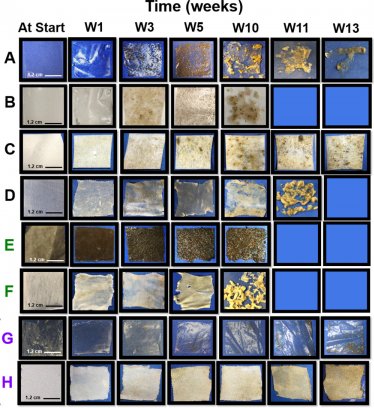
The study showed the comparative disintegration of similarly constructed fabrics under identical seawater conditions. Naia fabric completely disintegrated at 13 weeks, compared to cotton fabric at 11 weeks and polyester fabric, which showed no visual signs of disintegration throughout the 25-week incubation in a flow-through seawater mesocosm.
The Eastman Naia team works closely with global sustainability-focused organisations like Textile Exchange, Canopy, The Microfibre Consortium, Accelerating Circularity, Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals (ZDHC) and the Ellen Macarthur Foundation.
Naia is in the process of obtaining TÜV OK biodegradable marine certification from TÜV Austria and is already certified as biodegradable in freshwater and soil environments as well as compostable in industrial settings. Naia staple fibre is also compostable in home settings.
Image above: Time-lapse photography showing visual disintegration of certain materials (CDA and positive controls) and not others (negative controls) over a 25-week incubation in a continuous flow seawater mesocosm. Blue-filled boxes represent complete disintegration.: (A) 25 μm CDA film (no plasticizer), (B) 25 μm CDA film (triacetin), (C) 510 μm CDA foam, (D) 97 g/m2 CDA fabric, (E) 100 μm Kraft paper, (F) 91 g/m2 cotton fabric, (G) 25 μm LDPE film, and (H) 126 g/m2 PETE fabric.
Business intelligence for the fibre, textiles and apparel industries: technologies, innovations, markets, investments, trade policy, sourcing, strategy...
Find out more